The year 1994 turned the ideas of the scientific world upside down because a new concept was introduced into circulation: leptin. Since then, the fat mass is not regarded as an energy reservoir but is called a full-fledged endocrine organ, which, as it should be, is hormonally active: it produces leptin. The latter transmits information about the energy resources of the body to the brain, which decides how to spend it
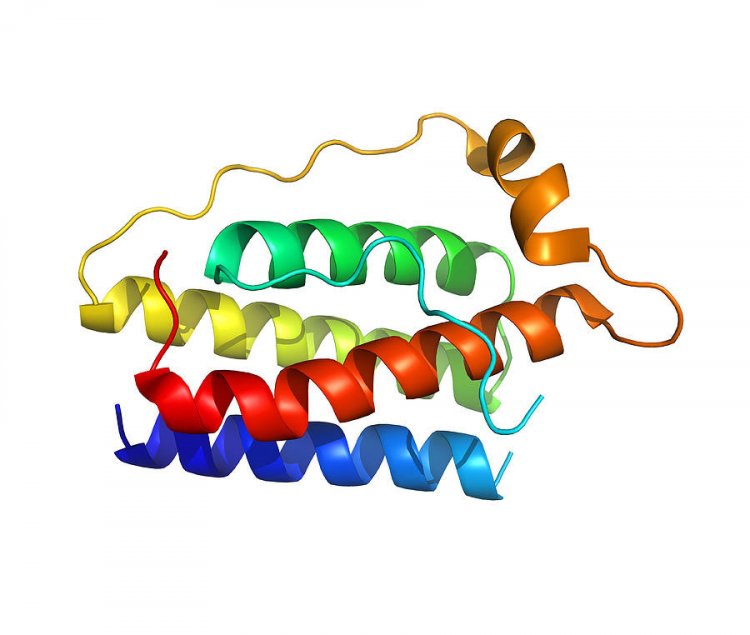
Leptin molecule
To put it a little more simply, it depends on leptin when we are hungry, whether we find the motivation or in what mood we wake up. And even this is not all.
Two modes and leptin
The leptin pathway looks like this: adipose tissue – blood – brain.
It is worth telling a little more about the “endpoint:” leptin gets to the hypothalamus, where special receptors and neurons that are sensitive to it are “waiting.” They are responsible for how our body will spend energy and what figure the floor scales will show. In this sense, leptin can be compared to a person who turns the arrows of a train when it reaches a fork: burn fat or accumulate “until better times.”
Moreover, the movement along the rails called “fat-burning” can occur at different speeds, or rather in one of two modes: abundance or scarcity. And again, leptin “decides” which one to choose.
Abundance mode
Here, energy is consumed as much as possible: we eat more, and we spend less. Hence the name of the mode. And then our body deposits extra calories in fat, and the level of leptin in the blood increases, which signals to the brain that it’s time to spend extra.
What happens to the body?
-
Metabolism becomes faster, fat actively breaks down;
-
The appetite decreases;
-
Activity, endurance, and performance get higher;
-
Mood and motivation increase;
-
Stress resistance and libido increase, the level of sex hormones becomes optimal;
- The immune system is strengthened.
Scarcity mode
This “path” is exactly the opposite. Here we spend a lot, but we consume little, so the level of leptin in the blood drops. The brain “thinks” that difficult times have begun and is reluctant to spend energy, and the body acts under the motto “survive at any cost.” Here, adipose tissue and its energy reserves are involved, which is why weight loss occurs: energy is taken from the inside, and not from food.
What happens to the body?
-
The appetite increases;
-
Motivation for any kind of activity and efficiency fall;
-
The mood worsens;
-
The immune system gets weaker;
-
The level of sex hormones decreases, libido level reduces.
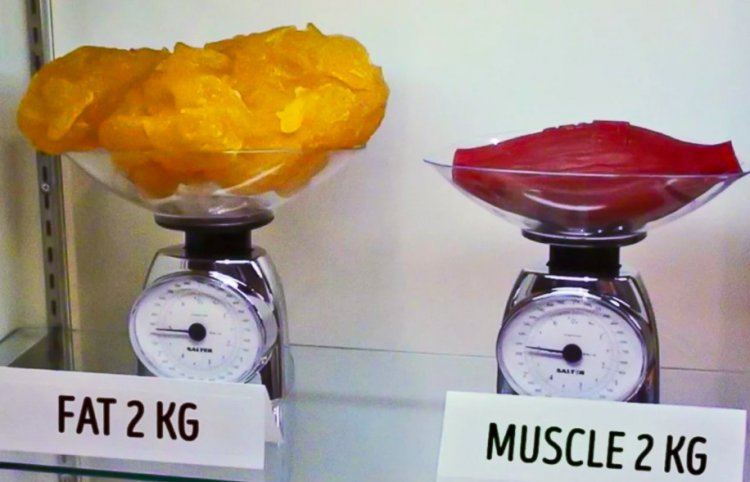
Such a regime has repeatedly saved the lives of our ancestors, and now, knowing such mechanisms, you can control them and change the percentage of fat in your body. The optimal amount of fat is 12–20% for men and 20–30% for women. In the second case, the percentage is higher, because women have a 40% higher level of leptin in the blood than men. The reason is in hormones: “male” testosterone reduces the secretion of leptin.
Strength and energy
From leptin, we came to adipose tissue, the largest source of energy. The body of an adult with 15 kg of adipose tissue contains more than 460 MJ (110 thousand kilocalories) of lipid “fuel” reserves. Such “baggage” can provide 8.37 MJ (2 thousand kilocalories) per day for about 2 months. Speaking scientifically, the reserves of triacylglycerols are spent, and the expenditure exceeds the consumption.
Adipose tissue is an extremely important part of our body. It helps to adapt to various conditions: hunger, stress, infections, as well as to significant excess of energy.
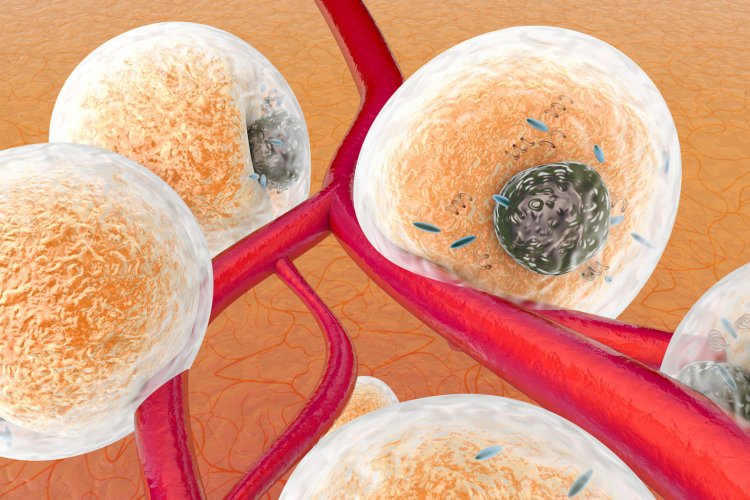
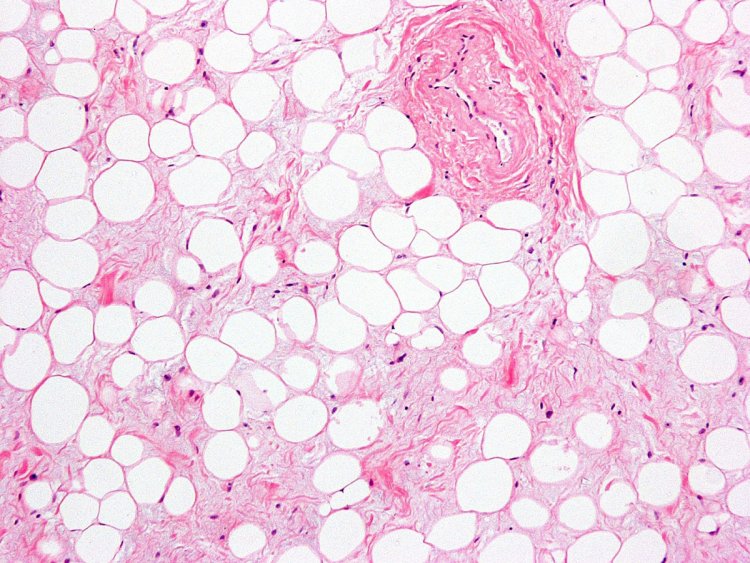
The fat structure is a heterogeneous tissue consisting of cells called adipocytes, as well as preadipocytes, leukocytes, monocytes, fibroblasts, macrophages, endothelial cells, and stem cells of the SVF type – stromal vascular fraction. Being an endocrine organ, it secretes adipokines, which perform important biological functions in the body:
-
regulating hunger and satiety;
-
maintaining the energy balance;
-
regulating carbohydrate and fat metabolism;
-
ensuring the functioning of vascular endothelium;
-
influencing the immune processes.
White adipose tissue
But at the same time, depending on the type of adipose tissue, the set of functions changes. According to research, there are three of them:
-
white adipose tissue (WAT);
-
brown adipose tissue (BAT);
-
pink adipose tissue, formed from subcutaneous fat in pregnant and breastfeeding women.
Brown adipose tissue got its name because of the mitochondria in its composition. Its task is to maintain a constant body temperature and use excess energy. And white adipose tissue stores energy in the form of triglycerides, which turn into a reserve source of energy in “hungry times.”
Adipose tissue is quite plastic, the percentage of fat content in the body varies depending on physical activity, diet, and even the environment. The main secret lies in the correct choice of an energy source.
Photo on the homepage: twitter
Photo on the page: anywellmag.com