Architecture changes along with people’s lives. Just some 20 years have radically changed the appearance of residential areas. We talked with Pavel Alekseevich Akimov, Rector of the Moscow State University of Civil Engineering, Member of the Russian Academy of Architecture and Construction Sciences, about how mathematical models are embodied in buildings, and why it is important to find a balance between skyscrapers aspiring to the sky and historical heritage
– The construction of a building is the work of many specialists. Who gets to work first?
Of course, an architect is the first to get to work: they perceive the wishes of customers about the construction of a particular project, perceive the plans, and fantasies how the future building and structure should look like. Then they try to implement it visually, on paper, so our architects need to be able to draw well, to have competencies in the field of engineering graphics. This is why to this day, drawing test remains an entrance requirement in architectural and construction universities.
Life does not stand still – an architect also deals with 3D modeling. One of the reports that are provided to the customer is a three-dimensional model of the building. Then the architect hands over the formed box and the walls, ceiling, and floor of the building to a design engineer, network specialists who analyze the durability, stability, and safety of the building or structure, determine the dimensions and options from which the structural elements will be formed. Then the turn comes for specialists in networks, ventilation, water supply, and sanitation, who determine the parameters of these communications, their location in the building, and, of course, an important specialist is a cost estimator. A huge number of specialists of various professions are involved in the construction of any site.
–But it all starts with an architect and an engineer?
Yes, it all starts with an architect and an engineer. I can say that at the Russian Academy of Architecture and Construction Sciences, where I worked from 2014 to 2019, my fellow architects always liked to say that an architect is the main builder, that’s why architects are perceived this way.
–An engineer and a builder deal with the exact mathematical part. How do mathematical models find their embodiment in buildings?
An important stage in the preparation of any construction solution is the design rationale of a building, structure, or complex. Various methods have always been used for this: analytical approaches, experimental studies. In the last 10 years, numerical methods that allow us to assess the strength, stability, and reliability of a building using a mathematical modeling apparatus have become quite firmly established in the practice of design specialists.
A mathematical model is the replacement of the building or structure itself with an idealized model, which we use in mathematical language.
This practice has been developing at our university for a long time. We had a computer center that dealt with design automation issues. Then, in the first decade of the 2000s, a Scientific and Educational Center for Computer Modeling was created. Now the specialists of our university are involved in the calculation of all the unique projects that have been built in recent years and are now being constructed. These are the facilities for the 2014 Olympics, almost all the stadiums for the 2018 World Cup, and almost all the high-rise buildings that are being built in the capital. The abundance of architectural forms imposes special obligations on the engineer: the more unique the form and the more complex the type of construction site, the more complex the calculation justification. There is a system of building codes and regulations, where everything seems to be regulated, but many issues remain beyond the scope of this system.
For example, there is a long-span building. Questions about the assessment of snow impacts, how the snow load spreads to the building’s levels, or what effect the wind load has on a high-rise construction with a height of several hundred meters. All this can be found out either using the mathematical apparatus of numerical modeling, or the apparatus of experimental modeling. For example, a wind tunnel, if we are talking about wind loads, which, by the way, is available at our university. But in any case, the most powerful tool is precisely mathematical modeling.
– Just as at one time computer-aided CAD design replaced pencils and Whatman paper, BIM is now being replaced by the technology of 3D modeling. Does this make the work easier?
This system is gradually being implemented. In general, the construction industry is very conservative. This is very good because the risk of mistakes is a risk for hundreds and thousands of people who live or work in a particular building or structure.
When I was studying, we had works that we performed on Whatman paper, but already then automated CAD design systems were being introduced, and so on, which replaced the usual drawing board and technical pen.
Now the construction industry is faced with the task of actively implementing an information modeling system or BIM technology. Moreover, from January 1, 2022, they will be mandatory at all construction sites of state orders.
Digital doubles are the next stage after BIM. We are talking about a geometric model, the same three-dimensional model of a building or structure, in alliance with the computational model mentioned above. All this unites the concept of a digital double, which must be considered not only at the stage of building construction, but also at different stages of the life cycle.
We strive for this, we try to introduce such disciplines for students, introduce them to advanced technologies of BIM solutions, mathematical modeling, and monitoring of an already built site. In the latter case, it is important to monitor both the condition of the construction and to assess situations that may cause a potential risk to the safety of the building.
– That is, very soon it will be possible to see the capital in the “digital?”
Everyone strives for this. But there is a lot of work underway to the ideal image that we are talking about.
– Now a lot of attention is paid to the development of artificial intelligence. For example, SGS has developed an AI-based construction monitoring system. Tell me, do such technologies justify themselves? Or is it better to assign the control duties to people?
In general, monitoring issues are very relevant and important for any unique project. But if we talk about best practices, it is important to provide a monitoring system for the construction of any high-rise building. This is a set of sensors that are placed in certain places. A variety of moments are monitored: movements between control points associated with the slope of a building or structure, deviations from design marks, and so on. Of course, it is not quite right to assign this only to the examination stage. Many things can be controlled only in automatic mode. Another thing is that the technologies themselves, without their proper understanding, also do not provide answers to questions and can lead to negative consequences. To design a monitoring system, you need to apply a serious intellectual foundation: correctly place the sensors, select equipment, and software that will monitor, among other things, the safety of this site. Of course, all this should be controlled by qualified personnel who can identify acute points and make preventive decisions to prevent emergencies.
– Is it possible that with the presence of artificial intelligence, the need for people's presence will disappear over time?
I think so. Although I am not a supporter of an overly optimistic view of the disappearance of many professions, which is now being seriously discussed. But, of course, there are professions in the construction industry that disappear over time because progress does not stand still. Another thing is that we try to train our personnel in such a way that they have, first of all, a powerful fundamental training, and then they can learn something new at the workplace. The most important role of any university is the need to instill in a person the desire to learn and master something new. If you have it, then it will not be difficult for you to cope with certain technological solutions.
–If we talk about Moscow, it is changing rapidly and radically. How important is it to maintain an architectural balance to preserve the historical appearance? For example, the Moscow City complex is radically different from the architecture of the 70s or even 90s.
The experience of working with Alexander Kuzmin, the former chief architect of Moscow, made me very attentive to such issues. In fact, it is difficult to imagine a city that has stopped developing. There is always something new. If we look at Moscow, it has been rebuilt several times. There were fires of the war of 1812. In the 15th century, they began to build the Moscow Kremlin in today’s form. Each generation brought something new.
If we talk about Moscow City, it is very important that it was decided to place it not within the Garden Ring, which would probably cause a huge discussion, but still outside the center. The goal was to relieve the center of Moscow from the influx of representatives of various commercial organizations and firms. It is a common practice to form such localized “cities,” and this center is put as the center of business activity, so it seems to me that Moscow City is a kind of business card of the city now, a demonstration of revolutionary solutions in the construction industry, including.
There is another question that often the construction of such high-rise buildings is not just a commercial project, but a question of reputation and the desire to perpetuate itself on the part of the customer. Everyone strives to build a building as high as possible, to get ahead, to set records in a particular area. This is a question of a certain image of the city and the country.
– Why are buildings so rapidly growing up? Is it true that this practice is gaining momentum in the world?
There are global assessments of specialists. As a rule, the development of high-rise construction is determined by two factors. Firstly, it is urbanization, and secondly, economic growth. As the city becomes the center of business activity, the value of land increases. In order to be able to accommodate as many different kinds of employees and organizations as possible, there is a need for upward growth.
This is also due to the economic factor. There are different expert assessments. For example, a 1% increase in global GDP leads to approximately the same increase in the number of skyscrapers in the world. The first skyscrapers appeared in Chicago and New York. These were huge centers of business activity. The growth of shares contributed to the development of high-rise construction. At the end of the last century, China and Hong Kong were actively developing. Now a significant part of high-rise construction is localized in these regions.
There are even studies demonstrating that the economically justified building height is also different for different regions. The economic efficiency of a building, its height are determined by the local labor market, local technologies, the cost of land. If you look at this cost-effectiveness curve depending on the height, it has a U-shaped appearance. Most of the buildings in the world have a height of about 200 meters. This is a kind of balanced indicator. In general, only a third of the states have high-rise construction. This is an indicator of the level of economic development and business activity in general.
– That is, Moscow City is a new trend, and soon all of Moscow will be like this?
I think that after all, no. This is a fairly localized area where there are still projects that have yet to be implemented. It seems to me that the concentration of such a large number of buildings in one place is consistent with global trends, but it does not apply to the entire territory of the capital.
– Is it economically profitable that people can both work and live in one place?
It is consistent with global trends. The only thing is that the task of unloading the center of Moscow and simplifying transport communications has not yet been solved to the extent that it was intended.
– Does the construction process change over time, or does something remain unchanged?
Of course, it changes. This can also be observed in the buildings around us. We all remember that everything began in the second half of the last century with mass panel construction. This was justified because it was necessary to provide as many citizens as possible with the opportunity to live in separate apartments. In principle, even now, if the developer is tasked with building residential areas in a short time and there are no restrictions in terms of resources, then panel construction is very often chosen.
In recent years, monolithic construction, monolithic-brick solutions, and modular buildings have been coming. Various additional structural and facade solutions are used. Slowly, but firmly innovations are entering the construction industry. The appearance of a contemporary building and, say, one that was built a hundred years ago is difficult to confuse.
– Now, in addition to the usual building methods, the use of modular construction technology has begun, when the structure is assembled not at a construction site, but a factory. How reliable is this?
You know, this year we managed to recreate the Board of Trustees of our university in a new form, which was headed by Deputy Prime Minister of the Russian Federation Marat Shakirzyanovich Khusnullin. It also includes many representatives of industry business companies. For example, one of the oldest partners of our university is the Monarch Group, which invests a lot of intellectual and financial resources in modular construction.
Of course, this is a very promising direction, which has many advantages. First – it is good that individual modules are manufactured at the plant because this allows us to ensure certain quality standards, which are sometimes very difficult to achieve on the construction site. There are separate solutions in which such modules even contain furniture, interior items, and so on. And there are solutions when a significant height of such buildings is achieved, it also allows you to save resources that are involved on the construction site. Construction time is also being reduced.
There is one drawback that everyone knows about – transport accessibility. Not every construction site can deliver such modules, especially when it comes to hard-to-reach regions.
If we talk about Moscow, the Monarch company has a plant that allows using advanced European technological solutions. I think that soon we will see in practice the implementation of this approach to modular construction at a new qualitative level in the capital.
In terms of safety, a lot of attention is paid to the modules, because they need to be transported and then lifted by cranes. During transportation, they may experience certain types of loads that are incomparable with those expected during the operation of the building. This also requires certain moments of reinforcement, so if the entire building is being assembled, then it should turn out to be reliable.
– Which country has the most successful experience in creating safe buildings?
In our country and in Soviet times there was a very powerful school of designers and calculators. I can give an example of Vladimir Ilyich Travush. He is the Vice-President of the Russian Academy of Architecture and Construction Sciences. He now works in the Gorproekt company. At one time, he was one of the authors of the Ostankino TV Tower, in recent years he was engaged in the Lakhta Center project in St. Petersburg. This is the tallest building in the world, built on marshy soils. Also, Moscow City is his project. In fact, the solutions used by our specialists and scientists in the field of construction sciences are rightfully among the most advanced. Of course, it is important to consider foreign experience, which is now being done in the industry. For example, we touched on the topic of mathematical modeling and information technologies. They came to us from the West, and this can only be welcomed.
In general, I want to say that the construction standards that are currently in place in the Russian Federation, its engineering school, and schools that form personnel for the industry are what distinguishes a serious country from one that can only focus on intellectual resources abroad.
– What is currently being studied in this area in science?
Many issues, relevant for the construction industry. These are issues of calculation justification, strength assessment, the safety of buildings and building structures. The structures themselves are also changing, more and more bold architectural solutions are being used. These are issues of construction materials science because new materials are used. Complex mathematical models are required to describe them, and this is a separate issue.
If we talk about our country, we have some very important segments of construction. These are, for example, hydraulic engineering construction, the construction of thermal and nuclear power plants. Issues related to the organization of construction works and construction technology on the site, issues related to the digitalization of construction are also relevant. There is also a completely separate direction: 3D printing of buildings and structures, which is actively developing in all countries. There are questions about the economy, issues related to complex safety in construction, fire safety. If we talk about the university, we have a scientific and technical complex, which includes more than 25 different scientific departments, institutes, centers. And security issues are the most important points in our work.
The construction industry is doomed to always remain among the most important.
It’s a difficult time right now, coronavirus. At all times, construction is usually the instrument of overcoming any crisis, the locomotive of the development of the state’s economy. This was the case in the United States during the Great Depression, and I think it will be so now.
In the industry as a whole, if we take our graduates, there are no problems with employment. Although the current situation in the labor market is not easy.
– Are young people trying to get into this field to do science?
We have many people who want to engage in practical activities and go to work on a construction site or deal with modeling issues in a design firm. Some stay to continue their studies in master’s and postgraduate studies, which we also welcome.
– Pavel Alekseevich, I can’t help but ask a question about the building in which we are now. It is even a complex that consists of buildings of different heights and shapes. Tell us, what is this project?
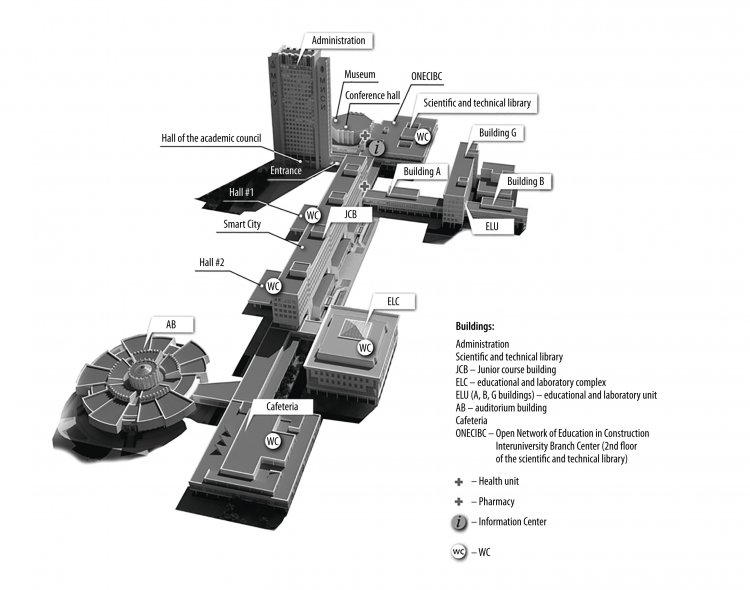
This is, indeed, a unique complex that began to form in the second half of the twentieth century. Great merit belongs to the former head of our university. Certain additions were made to this ensemble. For example, in 2016, an athletics arena was commissioned, in 2018 a swimming pool was built, a new academic building was built, the structures that are the pride of our scientific and technical complex were also completed, the same wind tunnel was improved, the appearance of the campus was improved. NRU MGSU is also a unique natural place – we are located near the Losiny Ostrov National Park. Everything here is concentrated quite locally: student dormitories are located not far from the buildings where the educational classes takes place. And our branch, which is in the city of Mytishchi, is within the accessibility zone, 15 minutes by car. Such a concentration of buildings and structures fully corresponds to the meaning that is now put into the campus concept. Our teachers and students who live in a hostel do not need to spend a lot of time moving from one place to another.
Of course, there is a lot to be done in the development of the campus. Now we are coordinating a project for the construction of a new dormitory for 960 places for our students. The Moscow government has supported us in the construction of an ice arena that will complement our sports cluster.
I believe that a university is not only an education but also a socio-cultural center.
I can say that the territory of our campus is very popular among the residents of the North-Eastern Administrative District. We hold many socially significant events, not only scientific and educational but also sports. This is the most important mission of any leading university.
– Does the expansion of the university territory and the construction of a new dormitory campus indicate that more and more young people want to become architects and builders?
Yes, and now these difficult stages of economic development strengthen the understanding of the parents of applicants, and the applicants themselves, that there are such professions that will always be in demand. The profession of an architect is one of them. No matter how economic circumstances develop, people still want to live in good, comfortable, and safe conditions, they always strive for their own housing, and construction solves all these problems.