Today, on May 20, the world marks the Day of Traumatologist. The holiday is devoted to physicians who, by the nature of their activities, not only save lives but perform complex surgical operations as well. Traumatology is one of the most ancient areas of medicine. It is commonly accepted that Hippocrates was its founding father.
On this day, various activities and events are organized comprising all those who have something to do with traumatology, including traumatologists, orthopedists, surgeons, producers of pharmaceutical and medical equipment, and supporting medical staff. The participants of these conferences and seminars talk about the results of new studies, cutting-edge achievements and technologies, the exiting problems and their possible solutions.
Translated from Greek, traumatology means teaching on traumatic injuries (trаumatos is the Greek for wound, injury, while logos is the Greek for teaching). In a narrower sense, word traumatology is applied to the section of clinical medicine studying the injuries of musculoskeletal system (bones, joints, muscles, ligaments and tendons) and skin covering.
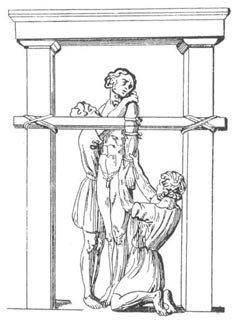
Hippocratic Plank – a lever device for correcting dislocations
Traumatology is one of the most ancient sections of clinical medicine. The history of it counts many centuries. The fact is that people might get injured at all times. Individual reports about the origins of surgery go back centuries. They have reached the present time only in the form of individual drawings, archeological findings, artifacts looking like surgical instruments and numerous rock inscriptions dated back to the 6th millennium B.C. It is known that back at that time, the ancient surgeons performed craniotomy and put in bandages in case of bone fracture to immobilize the patient. The examination of Egyptian mummies showed that the Egyptians used the immobilization of injured limbs several thousand years B.C. ago.
The papers by Hippocrates (460-377 B.C.) contain a classic description as to the symptoms and treatment of joint dislocations and bone fractures. Among the works by Hippocrates that have survived to the present day, there are Mochlicon (Reposition Methods) and Peri Arthron (On Joints) having a direct bearing on modern traumatology.
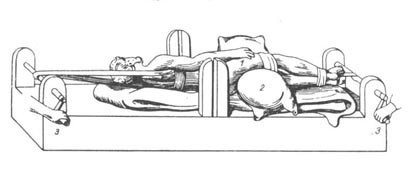
Hippocratic Bench. Correction of hip dislocation. 1 – injured limb; 2 – roller; 3 – reels moving in the opposite direction
He was the first to suggest the terms kiphosis and hyboma meaning hump. For the cases of shoulder dislocation, Hippocrates recommended six different methods of correction: manually, by heel, by shoulder, by pestle, by plank and on ladder. He described the methods of correcting hip and vertebral dislocation. Hippocrates pointed to the necessity of further immobilization and recommended various methods of fixation – with the help of wax, resin, leather and lead. The majority of recommendations by Hippocrates would be used by physician for many centuries. Some of them are even consistent with the principles of modern traumatology.
The periods of rapid development and implementation of treatment method in traumatology were related to traumatic cases that would occur in the course of military operations and natural calamities. In early 20th century, traumatology was spun off into an independent research and practical section of surgery. The reason behind it lay in growth of cities, industry and development of technologies which led to increase in traumatism, mortality and disableness due to severe industrial, road and household injuries.
The first domestic clinics and institutes
In Russia, spinning off orthopedics into independent area of medicine took place in late 19th – early 20th century. In 1895, a department of desmurgy and mechanurgy with professor Heinrich Turner (1858-1941) at the head was established under the Imperial Military Medical Academy. As early as in 1900, the professor opened the first orthopedic clinic in Russia.
In 1906, the first in Russia state orthopedic institute started its activities in Saint Petersburg. Military surgeon, orthopedist and former student of the Imperial Military Medical Academy Roman Verdun was appointed to the position of its director. At the same time, one more orthopedic institute was opened in the northern capital. It was founded by doctor of medicine Karl Horn. The work of this institution lay in not only treatment and research activities, but training medical specialists in the field of orthopedics a well.
The third domestic medical center dealing with orthopedics and traumatology was Physio-Mechanical Institute opened in 1907 in Kharkov. Orthopedist and traumatologist Karl Wagner became its founder and first director. His scholar papers included On the Origin of Peudarthrosis and Bone Fractures and Their Treatment. Guide for Physicians and Students.
At that very time, traumatology and orthopedics became independent disciplines of medicine. In 1920-1930s, national societies of orthopedic surgeons were founded. For instance, in 1929, the International Society of Orthopedic Surgery and Traumatology (SICOT) was established. At present, the organization comprises the specialists from over 110 countries.
The activities of traumatologists are directly related to the ones of surgeons, orthopedists, transplantologists, x-ray specialists and immunologists.
Sources:
International Day of Orthopedic Traumatologist.
Source of image in the text: The Day of Traumatologist in Russia: History of Holiday
Source of image on the homepage: Traumatology. Medical Center