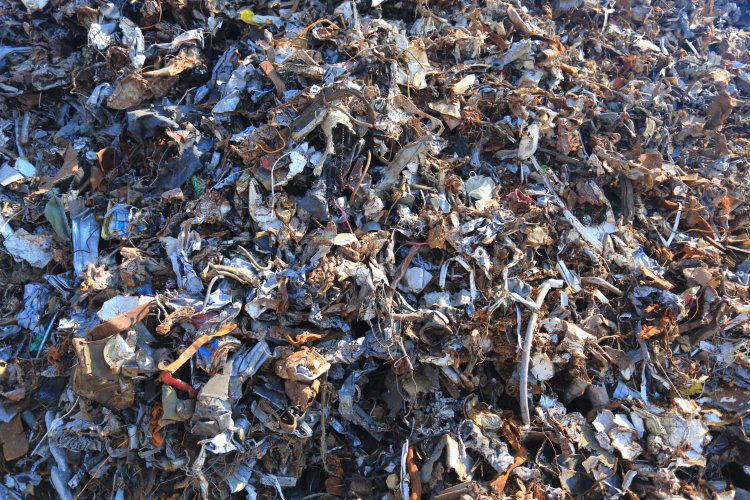
The height of ten-story buildings, the area the size of stadiums. After the introduction of the waste reform, the fight against hundreds of landfills in Russia began. The goal is the formation of sorting complexes, processing stations, and in the future – the construction of incinerators for burning waste. The landfills themselves are remediated – the lands are restored, returned to the ecological balance after many years of exposure to filtrate and landfill gases.
Read about the “chemistry” of garbage dumped into a single pile and technologies for landfill remediation.
The “chemistry” of garbage
In the same pile, there are leftovers of food and paper, iron and cut branches, an old fur coat, and worn tire: everything will be taken to landfills indiscriminately. In a multi-ton pile, under the pressure of the following layers, the waste begins a new chemical life.
Most of the garbage that ends up at the landfill is organic. About three-quarters of the waste can decompose and rot, starting new processes. They begin with aerobic degradation – while oxygen remains in the garbage, microorganisms break down chemical chains. As a result, what remains is an organic mass and a mixture of gases – mainly carbon dioxide and nitrogen.
At a certain point, there is no oxygen left in the pile – the existing one in the waste has been recycled, there is nowhere for a new one to come from: a load of new garbage is on top. Then anaerobic processes begin, which are also called methane fermentation. That’s when landfill gas is formed. First, acids and alcohols arise – these are intermediates, from which bacteria form acetates and hydrogen. Then the methanogens form methane from acetate, which makes up most of the landfill gas.
In parallel with the air chemistry, the filtrate is also formed in the garbage heap – water, passing through the rotting thickness of waste, turns into a solution of many chemical elements and compounds, including toxic ones. The filtrate appears in the warm season during rain, and in the cold, when snow on the pile melts due to heat from internal chemical processes. If the landfill construction technology is violated, the filtrate can get into the soil and water. Toxic substances poison living organisms, infect surface and groundwater.
Remediation stage
The purpose of remediation is to reduce the negative consequences of chemical processes that have been taking place for years in a dense garbage heap. After all the stages of remediation of the waste storage land, it can again be used for household needs without danger. The stages of remediation are divided into technical and biological.
At the technical stage, the polygon is brought to a new look. The landfill is leveled, if necessary, increasing its area, but reducing the height. To form a relief, ditches, depressions, and sinkholes are filled in, the perimeter of the polygon is strengthened. In parallel, drainage systems are being installed to collect filtrate and wastewater: in the process of forming a new landscape, it is important not to infect neighboring lands. Each landfill requires a separate project, for example, if a river flows next to a landfill, it is necessary to secure it.
Separately, degassers are installed – systems that remove dangerous landfill gas: it is toxic, flammable, and pollutes the air. Landfill gas is burned at some landfills – that’s why high torches are installed above the landfills. But modern technologies also allow us to process gas to use it in the future.
Gas production at the landfill can last for several decades, but over time the methane content in it decreases. Through vertical wells, the gas is removed to the scrubber treatment stations. This is a device that purifies gas through the water supply. Due to the operation’s relatively low cost, flushing is one of the most popular methods of gas purification. After that, the gas can be used to generate thermal energy by burning. Deeper purification and enrichment of gas allows to prepare a fuel mixture, including the one for engines, or use it in urban networks.
After the landscape of the new landfill is formed, the soil and surroundings are protected from the penetration of filtrate, and the gas is removed, the biological stage of remediation begins. This is the preparation of the fertile layer on the surface of the landfill, the preparation of perennial grasses and plants, their planting, and care for them.
The biological stage is set to improve the properties of the soil. Plants that are planted in a former landfill should have different properties depending on the location: be resistant to cold as well as exposure to toxic gas and drought. In parallel with taking care of the plants that restore the land, the accumulated filtrate is removed at the biological stage of reclamation, and harmful emissions from the landfill are monitored. This stage can last for decades, but with a competent approach to technology, it can take only a few years.
Based on open sources
Photo: juliannedev / ru.123rf.com